JAVA双亲委派模型-Parent Delegation Model
-
-
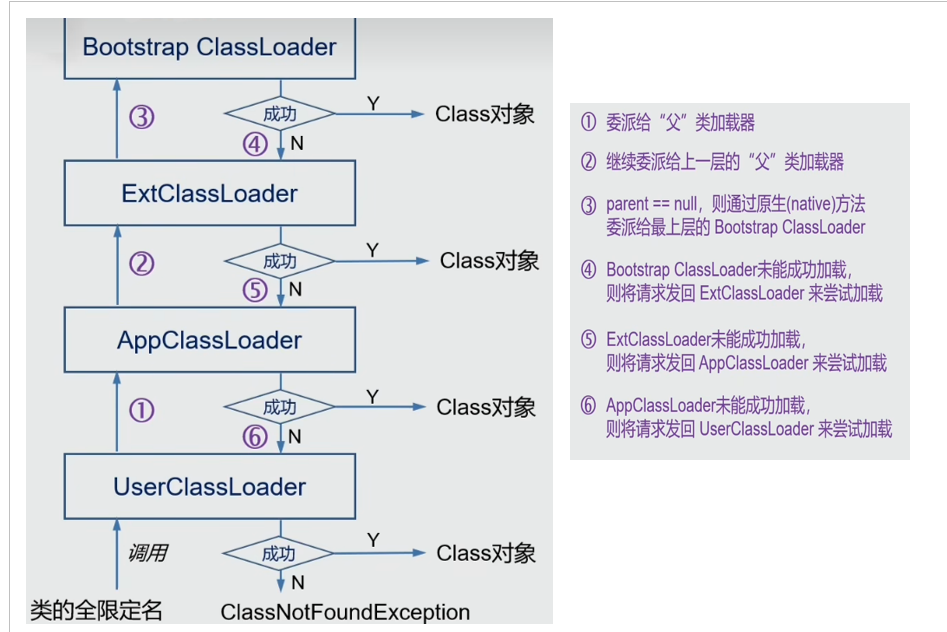
父子关系:双亲委派模型中,每个类加载器都有一个父类加载器(除了根类加载器),它们之间通过组合关系建立起层次结构。一个类加载器的父加载器通常是其上一级的加载器。
-
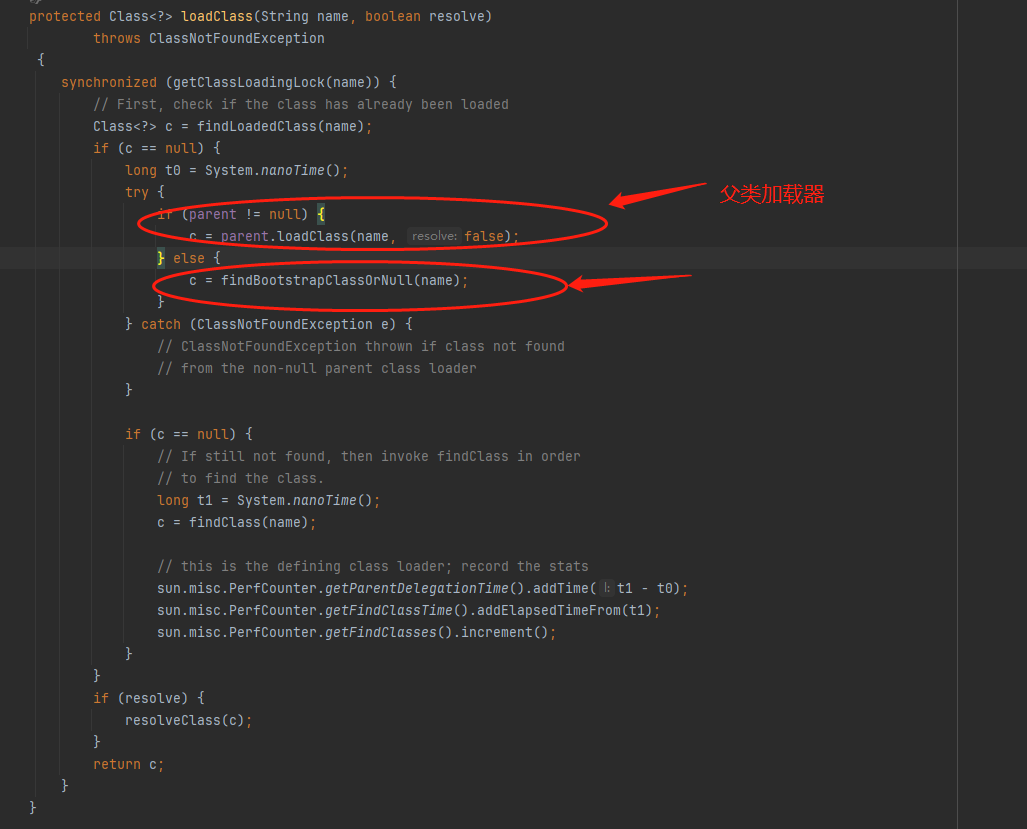
加载优先级:当一个类加载器需要加载一个类时,它首先将加载请求委派给其父类加载器。如果父加载器能够加载该类,那么就直接返回该类;否则,才由子加载器尝试加载。这样一层一层的委派下去,直到父加载器无法加载或者到达最顶层的启动类加载器。
-
避免重复加载:双亲委派模型的核心思想是避免重复加载类。在加载过程中,如果某个类已经由父类加载器加载过了,那么子类加载器就不再加载,直接使用父加载器已加载的版本。这样能够确保同一个类在内存中只有一份,避免了类的重复定义和冲突。
-
安全性保证:双亲委派模型也提供了一定的安全性保证。通过设置不同的类加载器层次结构,可以控制类加载的权限。核心的 Java API 类库通常由启动类加载器加载,而应用程序自定义的类则由应用程序类加载器加载。这样,核心类库的类无法被重新定义或篡改,保障了Java平台的稳定和安全。
-
/***
*从任意指定的某个目录中读取字节码类文件,然后创建对应的类
*/
public class CustomClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
static {
//当前的classLoader可并行加载不同的类
registerAsParallelCapable();
}
//指定的字节码类文件所在的目录路径
private final String customPath;
//构造函数,默认parent classloader是AppClassLoader
public CustomClassLoader(String customPath){
if(!customPath.isEmpty() && customPath.charAt(customPath.length() - 1)!= File.separatorChar){
customPath+=File.separatorChar;
}
this.customPath=customPath;
}
//构造函数,指定一个parent ClassLoader
public CustomClassLoader(String customPath,ClassLoader parent){
super(parent);
if(!customPath.isEmpty() && customPath.charAt(customPath.length() - 1)!= File.separatorChar){
customPath+=File.separatorChar;
}
this.customPath=customPath;
}
//覆盖父类的findClass()方法 从指定的目录查找字节码类文件,并创建加载对应的class对象
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
try{
byte[] b = loadClassFromFile(name);
Class<?> c = defineClass(name,b,0,b.length);
return c;
}catch(IOException ex){
throw new ClassNotFoundException(ex.getMessage());
}
}
byte[] loadClassFromFile(String name) throws IOException{
String fileName = name.replace('.', File.separatorChar)+".class";
String filePath = this.customPath+fileName;
try(InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()){
int nextValue;
while((nextValue=inputStream.read())!=-1){
baos.write(nextValue);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
}
}
}